Digital dental X-rays have become standard in many practices—but how do they actually compare to traditional film-based X-rays? It’s a question patients ask often, especially when safety, clarity, and comfort are top of mind.
Both types of X-rays are used to diagnose issues like tooth decay, bone loss, and infection, but they differ in how they’re taken, processed, and used during your visit. In this blog, we’ll break down the key differences between digital and traditional dental X-rays, what each option means for your care, and why your dentist’s recommendation is based on more than just technology.
At Elizabeth L. Wakim DDS, we use low-radiation digital imaging to support accurate diagnosis and more comfortable visits. Our goal is to deliver care that’s not only effective—but informed by the latest technology and tailored to your needs.
What Are Traditional Dental X-Rays?
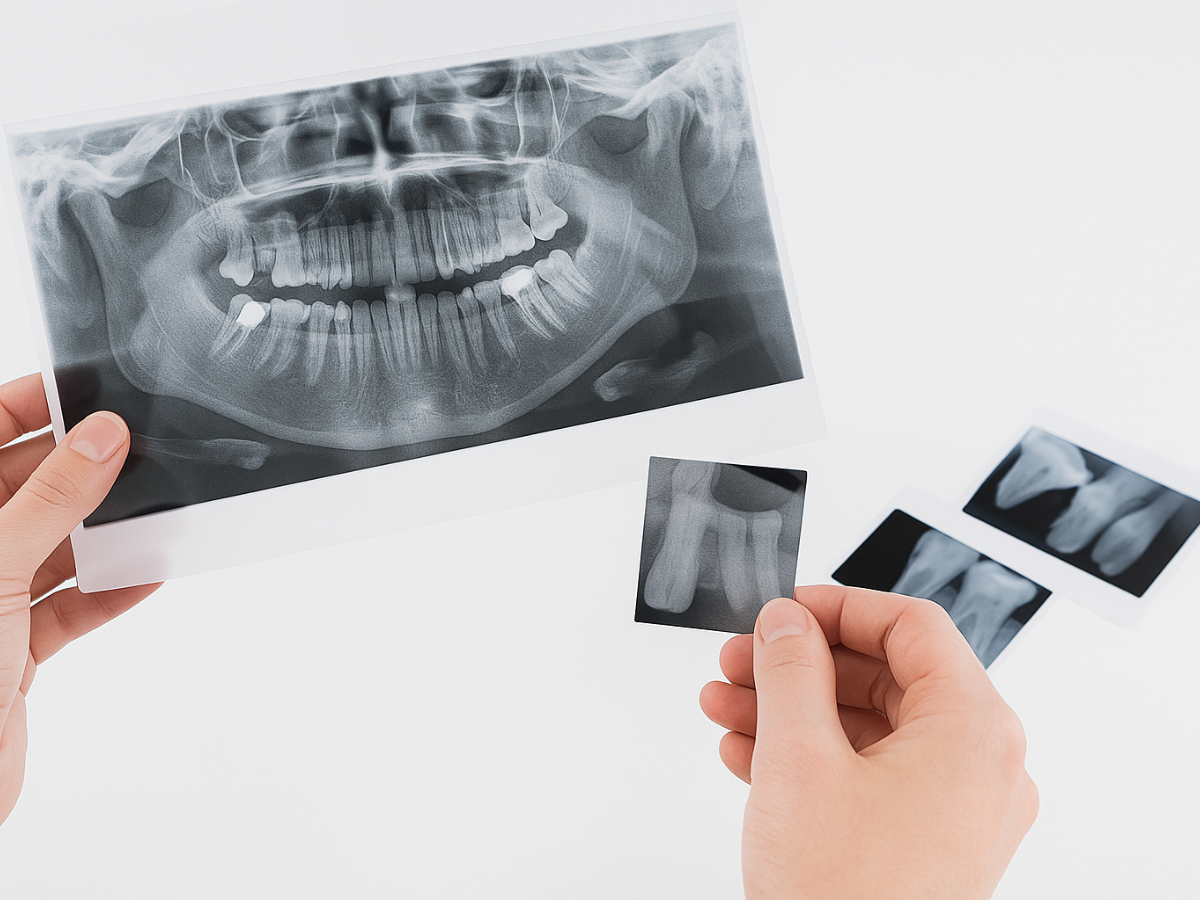
Traditional dental X-rays use photographic film to capture images of your teeth. Once the film is exposed using an X-ray machine, it’s developed using chemical processing—similar to how old camera film was developed. These images are then viewed on a lightbox or held up for visual examination.
While traditional X-rays have been used safely and effectively for decades, they come with some limitations. The process takes more time, uses higher levels of ionizing radiation, and lacks the ability to digitally enhance or enlarge images for closer analysis. Film-based X-rays are also harder to store, duplicate, or share between providers.
That said, they still offer diagnostic value in certain clinical settings, especially where digital equipment isn’t available or when a provider needs a physical record for reference.
What Are Digital Dental X-Rays?
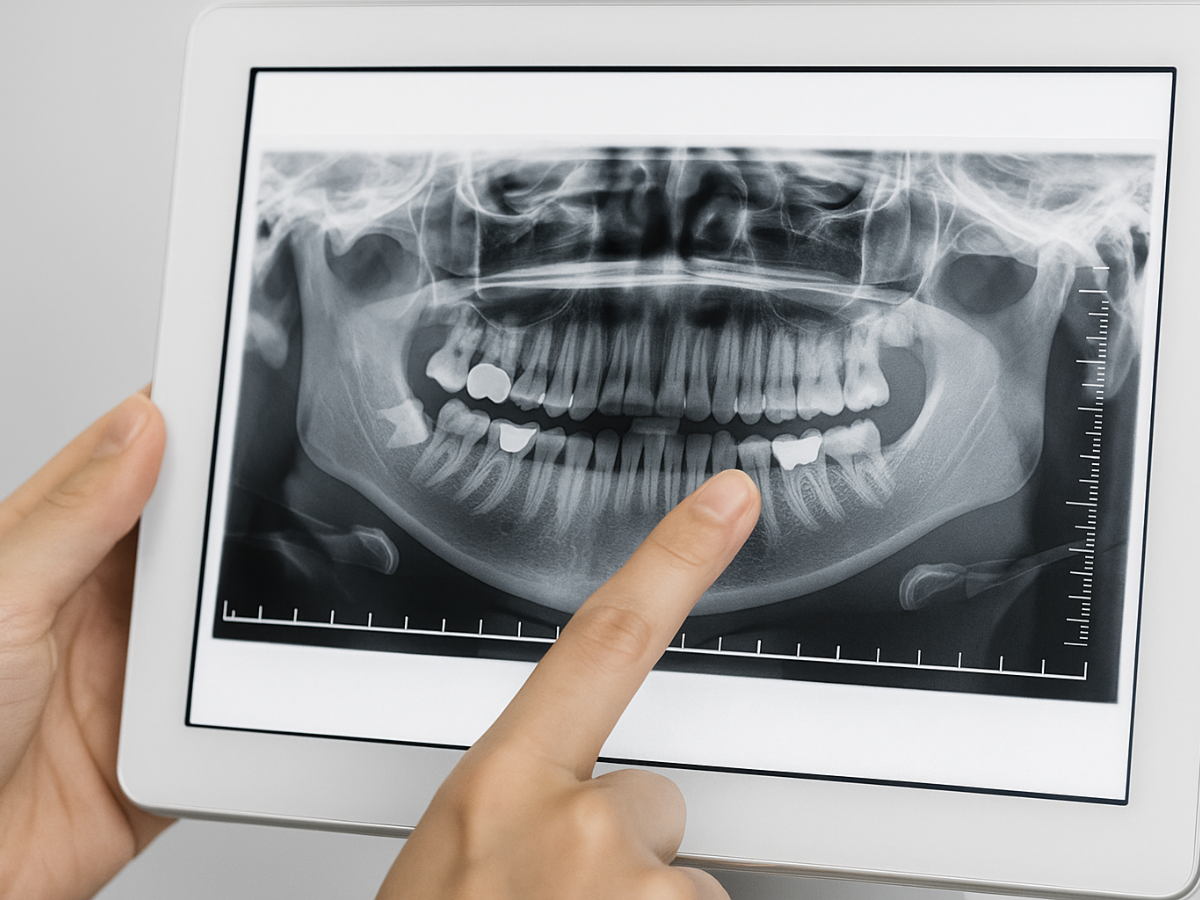
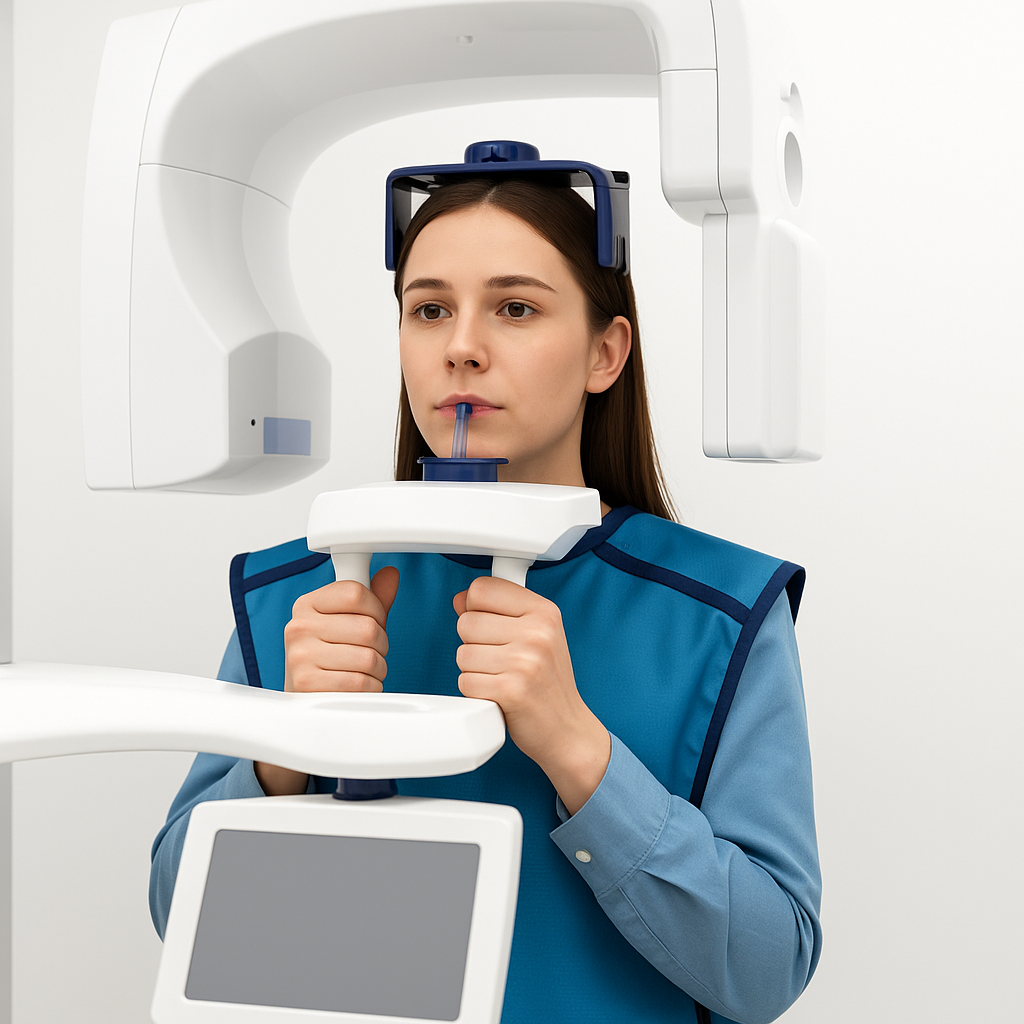
Digital dental X-rays use electronic sensors instead of traditional film to capture images of your teeth. These sensors are connected to a computer, allowing the image to appear on-screen almost instantly—no chemical processing required.
The technology offers several advantages. Digital X-rays expose patients to significantly less radiation than traditional methods. The images can also be enlarged, enhanced, or color-adjusted to help your dentist spot early signs of dental disease, tooth decay, or changes in bone structure with greater precision.
Because the files are digital, they can be stored easily, shared with specialists when needed, and compared over time to monitor progress or plan treatment.
Most modern dental offices have adopted digital imaging because it’s safer, faster, and more efficient for both patients and providers.
Key Differences Between Digital and Traditional X-Rays
While both types of X-rays help dentists detect conditions like tooth decay, bone loss, and infection, the way they’re captured and used during your visit can be very different. Here’s a side-by-side look at what sets them apart:
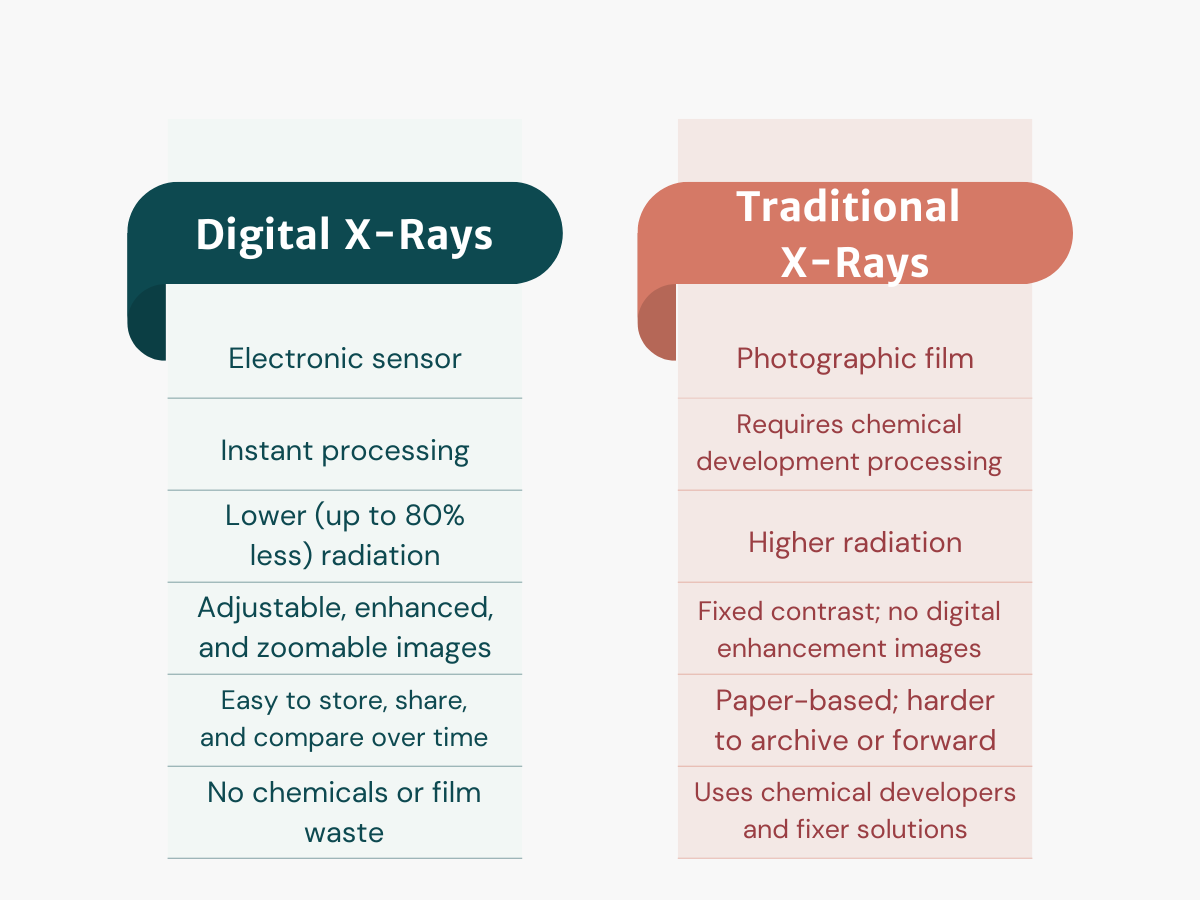
These differences help explain why many dental practices now prefer digital imaging, though traditional X-rays still have their place in certain situations. As part of routine care, both forms of imaging support early detection and better treatment outcomes. Regular dental checkups often include X-rays when needed, helping dentists monitor oral health and catch potential problems before they become serious.
Are Digital X-Rays Safer?
Yes—digital dental X-rays are considered safer than traditional film X-rays, primarily due to lower radiation exposure. In fact, digital radiography exposes patients to up to 80% less radiation compared to conventional radiography, making it a safer option for both the patient and the dental team—especially in cases that require frequent imaging, such as orthodontic treatment or root canal treatment.
All dental radiographs, whether digital or traditional, use ionizing radiation, so minimizing exposure is essential. Dentists follow strict safety protocols, including thyroid collars, lead aprons, and tailored schedules based on patient needs. This is especially important for younger patients or those at increased risk for cumulative exposure.
Because digital radiography produces instant images on a computer screen, it allows the dental team to check positioning and clarity right away. This also supports more accurate treatment planning, whether you’re addressing oral health issues, monitoring dental structures, or preparing for more complex care.
Regulatory bodies like the American Dental Association support digital dental imaging not only for its safety, but also for its efficiency, improved patient care, and ability to store digital files as part of long-term patient records.
When Might Traditional X-Rays Still Be Used?
While many practices now use digital radiography as their standard, there are still situations where traditional radiography or conventional film X-rays are used.
Some dental offices, especially those in rural or lower-volume areas, may still rely on traditional film X-rays due to budget constraints or the time needed to fully transition to digital systems. In certain cases, traditional methods also serve as a reliable backup when digital equipment is unavailable. While access to the latest technology can vary, many dentists continue to practice in rural communities—providing essential care where it’s needed most.
In rare instances, conventional radiography may also be used when extremely high-detail hard copies are needed for specific procedures or legal documentation. However, these cases are increasingly uncommon as digital dental imaging continues to improve in resolution and reliability.
It’s also worth noting that some dental professionals may still use X-ray film if they were trained exclusively on older ray systems, although many are now transitioning to computer technology that allows for instant image capture, easier storage, and better integration with modern treatment planning tools.
What Your Dentist Recommends Matters Most
Choosing between digital dental X-rays vs traditional methods isn’t just about equipment—it’s about what supports your diagnosis, treatment, and long-term oral health. Your dentist will consider several factors before recommending a specific type of X-ray:
- Your oral health history: Patients with a history of tooth decay, gum disease, or previous dental treatments may need more frequent or targeted dental radiographs.
- Your treatment needs: Imaging requirements vary depending on whether you need a routine exam, orthodontic treatment, a root canal, or implant planning. In many cases, digital radiography provides the fast, detailed images needed for precise treatment planning.
- Radiation safety considerations: If minimizing exposure is a priority—especially for children, pregnant patients, or those requiring frequent imaging—digital x-ray technology is often the preferred choice due to its lower radiation exposure.
- Office equipment and workflow: Some dental offices still use traditional radiography or conventional film as they transition to digital systems. In these cases, your dentist may still achieve accurate diagnostics using familiar X-ray film techniques.
- Image detail and accessibility: Digital dental imaging allows for immediate display on a computer screen, making it easier for your dentist to explain findings and involve you in your care. The ability to adjust brightness or zoom in on specific dental issues also enhances accuracy.
Better Imaging, Better Care
Both digital dental X-rays and traditional film X-rays serve the same purpose: helping your dentist detect problems early and plan effective treatment. The difference lies in how they’re captured, processed, and used to support your overall care.
Today, many practices rely on digital radiography for its speed, accuracy, and significantly lower radiation exposure. It’s a safe, patient-friendly option that supports everything from routine exams to complex treatment planning—without the delays or chemicals involved in film development.
Our team is committed to protecting your smile with gentle, personalized care. If you have questions about digital X-rays, radiation safety, or which imaging option is right for you, we’re here to help. Contact our office at (724) 558-8222 or use our contact form to schedule a visit and get expert support tailored to your oral health needs.

Dr. Elizabeth Wakim, DDS, is the founder of Enhanced Wellness. She’s a compassionate and highly-regarded dentist with her own practice in Washington, Pennsylvania, known for providing modern, comprehensive dental care, botox and facial aesthetics with a focus on patient comfort and anxiety reduction, serving general, cosmetic, and pediatric dentistry needs.